What is Scarcity in Economics?
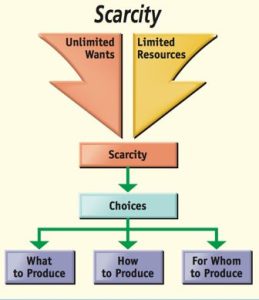
In economics, scarcity refers to the fundamental concept that resources, including time, money, natural resources, and labor, are limited in supply relative to the unlimited wants and needs of individuals and society. Scarcity is a pervasive and unavoidable condition in the field of economics, and it is the driving force behind the need for decision-making, resource allocation, and trade-offs.
Key points to understand about scarcity in economics:
Limited Resources: Scarcity arises because resources are finite. There are only so many raw materials, human hours, and financial capital available at any given time.
Unlimited Wants: On the other hand, human wants and needs are essentially infinite. People desire goods and services that can enhance their well-being, and these desires are not easily satisfied because there’s always something more that people could want or need.
Trade-Offs: Due to scarcity, individuals, businesses, and governments must make choices about how to allocate their limited resources. This involves making trade-offs, where the use of resources for one purpose means sacrificing their use for another.
Opportunity Cost: Every choice involves an opportunity cost, which is the value of the next best alternative that must be forgone when a decision is made. It’s the cost of what you give up when you choose one option over another.
Efficiency and Equity: The concept of scarcity is central to discussions of economic efficiency and equity. Efficiency involves getting the most value out of scarce resources, while equity concerns the fairness of resource distribution among individuals and groups.
Market Mechanisms: Markets are an important mechanism for allocating resources in response to scarcity. Prices in competitive markets adjust based on supply and demand, helping to allocate resources to their most valued uses.
Government Intervention: In some cases, governments may intervene in markets to address issues related to scarcity. This can include regulation, taxation, subsidies, and public provision of certain goods and services.
Understanding the Concept of Scarcity
Scarcity, in its simplest form, refers to the limited availability of resources compared to the unlimited wants and needs of society. It is the stark realization that we live in a world with finite resources, and these resources must be allocated efficiently to satisfy the diverse needs of individuals and society as a whole.
The Role of Scarcity in Economics
Scarcity is the cornerstone of economic analysis. It is the driving force behind the allocation of resources, the prices of goods and services, and the choices individuals and businesses make daily. Economists study scarcity to better understand how it influences decision-making and resource distribution. Also, read about How Long Does It Take to Get to Space
Scarcity and Resource Allocation
One of the most significant impacts of scarcity is its role in resource allocation. Scarce resources force individuals and organizations to make choices. This leads to the concept of opportunity cost, where choosing one option means forgoing another. The efficient allocation of resources is crucial in achieving economic growth and maximizing welfare.
Factors Contributing to Scarcity
Scarcity is not solely about limited resources; it is also influenced by factors like population growth, technological advancements, and environmental changes. Understanding these factors helps us grasp the dynamic nature of scarcity.
Opportunity Cost and Scarcity
Opportunity cost is a key concept in economics closely linked to scarcity. It represents the value of the next best alternative forgone when a choice is made. In a world of scarcity, every decision carries an opportunity cost, highlighting the importance of making informed choices. For more interesting information visit our website generalquests.com
Scarcity’s Impact on Pricing
Scarcity directly affects prices. When resources are scarce, their value increases. This phenomenon is essential in understanding supply and demand dynamics, as well as how businesses set prices in the market.
Scarcity in Everyday Life
Scarcity is not confined to economics textbooks. It permeates our daily lives, from budgeting household expenses to choosing a career path. We make choices based on what resources are available and what we value most.
Coping with Scarcity: Strategies and Solutions
Individuals, businesses, and governments employ various strategies to cope with scarcity. These strategies include conservation, innovation, and government policies. Examining these approaches sheds light on how we address scarcity challenges.
Case Studies: Scarcity in Action
Real-world examples of scarcity can be found in various industries, such as water shortages in California or the allocation of medical resources during a pandemic. These case studies illustrate how scarcity influences decision-making and resource allocation.
Government Intervention and Scarcity
Governments often intervene in markets to address scarcity-related issues. We’ll explore the role of government policies, regulations, and subsidies in mitigating the effects of scarcity.
The Global Perspective on Scarcity
Scarcity is not limited to a single region or country. It is a global issue that affects nations worldwide. Understanding the global dimension of scarcity is crucial for international cooperation and resource management.

Scarcity and Sustainability
As the world faces environmental challenges, the concept of sustainability becomes increasingly important. Balancing resource use and preserving the planet for future generations is a key aspect of addressing scarcity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, scarcity is a pervasive force that drives economic decisions and resource allocation. Understanding its profound impact on our lives is essential for making informed choices and creating a more sustainable future. By acknowledging the realities of scarcity, we can work towards a world where resources are allocated efficiently, and the needs of all are met.
FAQs
1. How does scarcity affect the prices of goods and services?
Scarcity leads to an increase in the prices of goods and services, as limited resources drive up their value in the market.
2. Are there solutions to cope with scarcity at the individual level?
Individuals can cope with scarcity by budgeting, conserving resources, and making informed choices based on their priorities.
3. What is the role of government in addressing scarcity?
Governments play a crucial role in addressing scarcity through policies, regulations, and interventions to ensure resource allocation is equitable and sustainable.
4. How does scarcity relate to sustainability?
Scarcity is closely related to sustainability, as it highlights the importance of preserving resources for future generations and protecting the environment.
5. What are some future trends in dealing with scarcity?
Future trends in addressing scarcity include advancements in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and innovative solutions to resource management.







